In this paper show that we can use the geometry of a 3-sphere to correctly calculate the radius of the observable universe. It is equal to the cube root of 12 pi times ct:
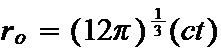
And that value equals 46.27 billion light years. The correct value.
The primary point of the paper is that we can use the geometry of a 3-sphere to calculate this radius. And to do it, we must use the 2c expansion rate and the radius of the hyperverse.